Ethernet Cable Types Explained: Categories From 3 to 8
October 3, 2022
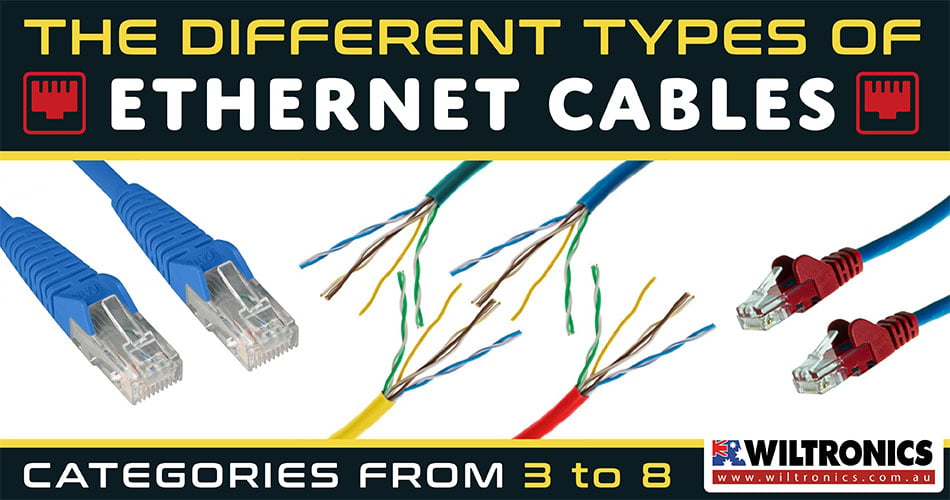
It is to your advantage to know the different Ethernet cable types = no more cabling headaches!
TLDR – Which Ethernet Cable Should I Buy?
Just need a cable to connect devices to the modem/router in your home or small office? A Cat6 Ethernet Cable is probably what you are looking for.
Wiltronics supplies these patch leads with RJ45 connectors in a variety of sizes, and a large range of colours for easy identification. Why just get blue, gray or black when you can get green, pink, orange, red, purple, and more!
When it comes to cables, it is easy to get lost. With so many wires to choose from, there’s a lot to learn about Ethernet Cables, aka Network Cables.
“Ethernet cable” is a general term, and you need to be more specific to find the right one for your needs. This is particularly important if you are looking for a network connection solution.
For one, you may notice they are nearly always classified as Cat + a number. The number that follows indicates the specification version supported by the cable.
Different varieties are available and common categories include Cat 5, 5e, 6, and 6a. You may have also heard the term RJ45. There is no need to learn deeper what is inside or on the connectors, although it can be very helpful.
An understanding of Ethernet cable types is what this guide is about. It also includes tips for choosing the suitable cable for the right application. Read ahead!
Ethernet and Network Cables Explained
Ethernet cables are everywhere, they are vital components when creating a home or business network.
Or simply for setting up Internet connections. But what are they, what do they do, and why do you need them?
The Ethernet connects computers and other network devices in a physical space, a.k.a. a local area network (LAN). And this is where the idea of an Ethernet network comes in.
It enables computers and other devices to share files, information and data efficiently. But to ultimately achieve this, you will need cables, cue Ethernet cables.
An Ethernet cable is a popular type of network cable. It is designed to work with Ethernet ports.
It runs from a router, modem, or network switch and comes in handy for wired networks that connect devices to the Internet.
More About Ethernet Cables
Ethernet cables have a similar appearance to phone cables. Except they feature double the amount of wires to a phone cable (8 vs 4).
Moreover, the connector is slightly bigger and with a small modular plug at the end of each cable. The small lever on the top helps secure and unclip the Ethernet cable.
So, when you push the cable into the port, it should click into place. Some units have LEDs that light up when successfully connected.
Ethernet cables also vary in length, from 0.3 to 30 metres and beyond. It is also possible to cut the cables to your preferred length.
They come in various colours, too, but they all work the same. Put this feature to use if you want to colour coordinate for easy cable management.
How Do Ethernet Cables Work?
Ethernet cables are plugged into ports to provide Internet or connect devices to a LAN. The most common use is connecting a WiFi router or modem to the Internet entry port or telephone line.
They can also be used to hardwire devices, such as TVs and computers, that need a network or Internet to work. When connecting to home or office LANs, most rely on twisted wire pairs.
Twisting the wires together enables the currents to balance.One wire has a current moving in one direction and the other going the opposite way.
This allows the overall fields around the twisted pair to cancel out. The data can then be transmitted over considerable lengths without additional precautions.
Ethernet Cable Types
There are several Ethernet cable types and categories on the market:

Straight-through (patch cables)
Straight-through cables are used to connect different types of devices. For instance, a computer to a router.

Crossover cables
Crossover cables are used to connect two devices of the same kind, e.g. connecting two computers.
These cables are far less relevant now, as technology improvements have almost eliminated the need for them. In most cases, a standard straight-through patch lead will do the job.
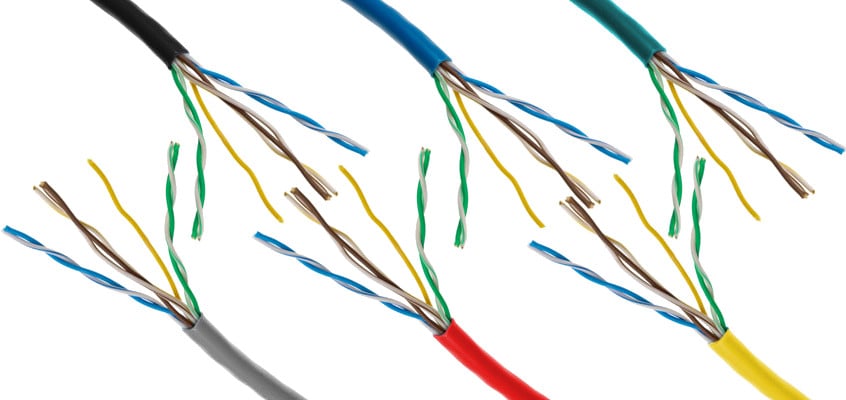
Solid cables
Solid cables are generally used for business networks, featuring a single wire run. They offer slightly better service and are cheaper than their stranded counterparts.
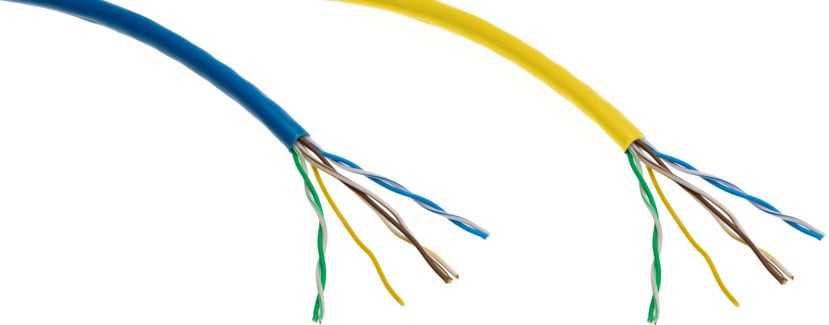
Stranded cables
Stranded cables contain a few smaller wires which work together. Most patch cables are stranded cables. They are more robust and better suited for home use.

Gel Filled Cable
Ideal for outdoor or direct bury installations where you need moisture resistant cable.
Shielding Initialisms
UTP = Unshielded Twisted Pairs. Suitable for most applications where interference is not a potential risk.
STP = Shielded Twisted Pairs. If there is a risk of interference, ethernet cables with shielding are recommended.
SSTP = Ethernet cables with two layers of shielding. The first is around each twisted pair, and the second is around all the pairs together. Also known as SFTP (Shielded/Foiled Twisted Pair). Use these in situations with the highest risk of interference.
LSZH = Low Smoke Zero Halogen. When exposed to high heat, this kind of jacket emits limited halogen and no smoke.
Ethernet Cable Categories
Ethernet cable types come in different variations—also known as Categories or Cat. Each category refers to various sets of standards. As these standards change over time, new Cats are created.
Wiltronics recommends Cat6 as standard, you can find our full range of Cat6 ethernet cable here. Cat5e and Cat6a ethernet cables are also available.
Anything lower than Cat5 is outdated and is not recommended for use.
Cat7 and higher are still uncommon and quite dear. Their speeds are far beyond what Australian internet speeds are currently capable of and thus provide no benefit. If you want to future proof your installation, we recommend Cat6a cable.
Category 3 (Cat3)
Used for voice and data communications in computer and telecommunication networks. Cat3 cables are a type of unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable.
Category 4 (Cat4)
The fourth-lowest grade of unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cabling. It can support internet speeds of only 10Base-T and is lower quality than CAT5.
Category 5 (Cat5)
An older form of Ethernet cable with a speed of up to 100 Mbps. Although not standardised, Cat5 cable typically uses 1.5 – 2 twists per centimetre.
Not recommended for new installations.
Category 5e (Cat5e)
Maximum Data Transfer Speed: 1 Gbps.
An updated version of Cat5, the e stands for Enhanced. It is recognised by the TIA/EIA and is defined in TIA/EIA-568, being last revised in 2001.
Moreover, it allows for faster speeds with reduced interference from electrical cables.
For connecting devices, get Cat5e Ethernet Patch Cables here. Available in lengths from 50cm to 20m in various colours.
Get your Cat5e network cables for cable installations from us! Various colours are available and also in different quantities. You can purchase by the metre or save in bulk with our 100m and 305m boxes.
Category 6 (Cat6)
Maximum Data Transfer Speed: 10 Gbps up to 55 metres, 1 Gbps up to 100m.
Enables speeds of up to 10 gigabits, depending on the area. It has thin wires, which helps its signal-to-noise ratio.
However the cables are stiffer than Cat5e cables, making them harder to run around tight corners.
Get your Cat6 network cables for cable installations from us! Our range includes Gel Filled, Solid, Shielded, and Stranded Cables. Available by the metre and in bulk quantities.
Or, for connecting devices, find Cat6 Ethernet Patch Cables here. They are available in a massive range of colours and lengths.
Category 6a (Cat6a)
Maximum Data Transfer Speed: 10 Gbps
An improved version of the Cat6 cable. The “a” in Cat 6a stands for “Augmented”, and the standard was revised in 2008.
It enables speeds of up to 10 gigabits per second. It also offers double the bandwidth as Cat6 and is often shielded. This helps reduce electrical noise and electromagnetic radiation from affecting the signals.
You can find our range of Cat6a Ethernet Cables here.
Category 7 (Cat7)
Cat7 twisted cables must be fully-shielded. That way, they can cut crosstalk and improve electrical noise resistance. It can offer up to 10Gbps (Gigabits per second) up to a 15-metre distance.
Category 8 (Cat8)
Cat8 is specifically designed for Data Centres and enterprise networks. Allows 2000MHz bandwidth and speeds of 40Gbps. It tends to be more expensive, though.
Ethernet Cable Connectors
RJ45 connector
RJ45 (registered jack) is an 8-pin plug that connects computers to Ethernet-based LAN. It looks similar to a telephone jack but is a bit wider.
Computers, printers, and network storage devices are a few of those that can use an RJ45. Get your RJ45 Patch Leads from us! A diverse range of RJ45 patches leads in various colours and lengths. Available in Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, and Cat6a SSTP.
We also have a wide selection of RJ Connectors, Outlets & Splitters.
Choosing the Right Ethernet Cable
The easiest way to select a cable is to pick one with the range and performance you need. Follow these steps or tips to get started:
Step 1
Consider the speed of your home Internet connection. The cable will not enhance your data speed, it will only carry as much data as your internet gives it. Cat6a may be worthwhile if you want to future proof your installation, but Cat6 or even Cat5e will be more than enough to cover most internet connections. Anything lower than Cat5 is likely to create a bottleneck, as it isn’t able to carry the data at the speeds your internet provides. This results in the illusion of slower internet.
Step 2
If you do not know your Internet speed, connect your PC to the modem and use a speed test. Doing so will give you an idea of what you will need for wired connectivity.
Step 3
Next, consider the speed needed for your network. Suppose you frequently move big files between computers or stream high-bandwidth video. A better Ethernet cable can make a huge difference.
If you do not need to move large files around, a fast in-home network is unnecessary.
Step 4
If you are looking for a replacement cable, go for recent versions to take advantage of speeds. Plus, future-proof your setup for years to come.
That usually means picking a Cat6 or Cat6a cable. A suitable cable can work together with other high-end network devices. This ensures that your connection is as strong as possible.
Note: Higher numbers represent faster speeds and higher frequencies, measured in megahertz (MHz). Newer cables support higher bandwidths and thus increased download speeds and faster connections.
The Bottom Line
Figuring out which Ethernet cable types work for you can be tricky, especially if you are new to them. If needed, our explainer above can be a good starting point.
Then you are more likely to choose the best Ethernet cable types for your home or work environment needs!
Tip: For a business network, go for the highest cable type to get the best results. For a home network, opt a cable that delivers the speeds promised by your Internet provider.
© Electrotech Brands Pty Ltd 2022


Write a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.