A Beginner’s Guide to Telephone Cables
April 28, 2023

Telephone cables transmit telephone signals from one location to another. They are made up of copper wires, twisted together and insulated with a plastic coating. The protective covering helps prevent interference and damage.
The public switched telephone network (PTSN) plays a big part in the setup. It is a global network of interconnected telephone lines. It enables people to make phone calls regardless of their location. When you pick up the phone and dial a number, your phone sends a signal through the PSTN. This will then connect you to the person you are calling.
The cables are usually underground or on poles to connect homes to the telephone network. Telephone cables may also be utilised for internet connections, transmitting data signals. This makes them vital in the interconnected world.
Besides transmitting voice and data signals, telephone cables can also carry electrical power. This process, Power over Ethernet (PoE), commonly powers devices such as IP phones, security cameras, and more.
This only proves that telephone cables are the backbone of our connected world.
The Uses of Telephone Cables
Telephone cables have a wide range of uses beyond just landline telephones. Without them, many of the technologies we rely on today would not be possible. This type of cabling also comes in handy in:
Internet connection
Telephone cables are can create a DSL (digital subscriber line) connection. DSL is a type of internet connection that uses telephone lines to transmit data. This allows you to access the internet without needing a separate cable or fibre optic line.
Cable television
Cable companies use an HFC (hybrid fibre-coaxial) network to transmit television signals. This network uses a combination of fibre optic and coaxial cables. In return, both deliver television programming to your home. The coaxial cable part of the network is made up of telephone cables.
Security system
Many security systems use landline telephones to connect to monitoring centres. When the alarm is triggered, the telephone line sends a signal to the monitoring centre. This allows the monitoring centre to take action if necessary.
Medical equipment
Many medical devices, such as EKG machines, use telephone cables to transmit data. This data is sent to a computer or monitoring station. Then, medical professionals can review it and make decisions about patient care.
Different Types of Telephone Cables
Telephones have been around for over a century. The cables that connect them have also evolved over time. Today, there are different types of telephone and data cables for various purposes. Understanding each can help you choose the right cable for your communication needs.
1. Coaxial cable
Coaxial cables are ideal for cable television and broadband internet. They have a copper core surrounded by layers of insulation and braided shielding. The shielding helps to reduce interference from other electronic devices, thus improving signal quality.
2. Twisted pair cable
Twisted pair cables are used for traditional landline telephones and Ethernet networks. They consist of two copper wires twisted together. The design helps to reduce interference.
3. Fibre optic cable
Fibre optic cables are used for high-speed internet and digital telephone services. They consist of thin strands of glass or plastic that transmit data using light signals. Fibre optic cables can also transmit data over long distances without losing signal strength. Thus making them ideal for long-distance communication.
4. Shielded twisted pair cable
Shielded twisted pair cables are similar to twisted pair. Except that the shielded type offers an extra layer of shielding. They are commonly used for Ethernet networks and can support data transfer speeds of up to 10 Gbps.
5. Multi-pair cable
Multi-pair cables are used for telephone systems that require multiple lines. They consist of several twisted pairs of wires housed in a single cable. Multi-pair cables can also support up to 25 lines, making them ideal for large offices or call centres.
6. Cat5e and Cat6 cables
Cat5e and Cat6 cables are used for Ethernet networks. They can support data transfer speeds of up to 1 Gbps and 10 Gbps. They are made of twisted pairs of copper wires and have a plastic coating.
Round vs Modular Telephone Cables
Round and modular cables are both used for telecommunications. But what are the differences?
Round cables are traditional types made up of a bundle of wires twisted together in a circular shape. They are ideal for telephone lines that require a lot of wires. This includes those used in businesses or large residential buildings.

2 Pair Telephone Cable Round
No longer available
Suitable for the connection of apparatus working on DC or voice frequency signals. Plain copper wire conductors with PVC-V75 cream-coloured sheaths for internal use. Conductor 1/0.5mm copper wire.
Modular cables, in contrast, are flat and have connectors on the ends. These cables are commonly used for home telephone lines and are also easy to install and replace.
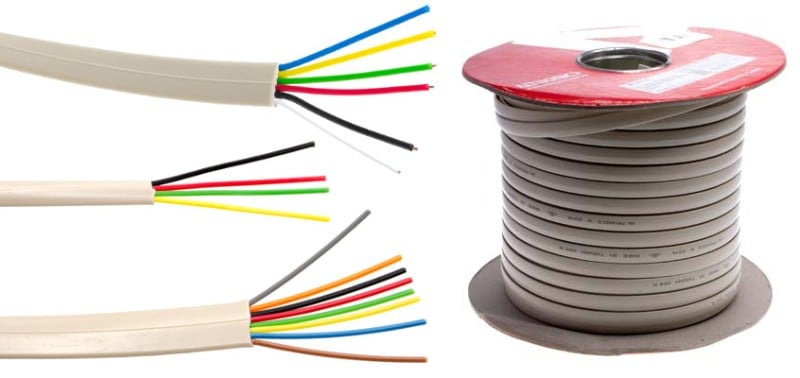
Telephone Cables Modular Flat
Ideal for the connection of apparatus working on DC or voice frequency signals. Plain copper wire conductors with PVC-V75 cream-coloured sheaths for internal use. Available in 4 Core, 6 Core, and 8 Core.
The choice between the two depends on your needs and the type of telephone system.
The Bottom Line
By understanding telephone cables, you can ensure your communication systems are:
- efficient
- reliable
- secure
You can also make informed decisions about their communication infrastructure. This includes the type of cable to use for a certain network, the distance, and the speed and quality.
© Electrotech Brands Pty Ltd 2023


Write a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.